China is, by a very wide margin, the world's leading producer of carbon dioxide emissions. No other nation has ever put as much carbon dioxide into the Earth's atmosphere in a single year as China. That includes the United States, the world's second largest producer of carbon dioxide emissions.
These statements are based upon data provided by Global Carbon Project for 2022, which reports historical data for national fossil fuel-based emissions of carbon dioxide from 1850 through 2021. In that most recent year, China added some 3,131 metric tonnes of carbon (MtC) to the Earth's atmosphere, while the U.S. added 43% of that amount. U.S. carbon dioxide output peaked in 2005 at 1,675 MtC and has generally fallen in the years since, while China surpassed that level in 2006 and has continued to increase its CO₂ emissions each year.
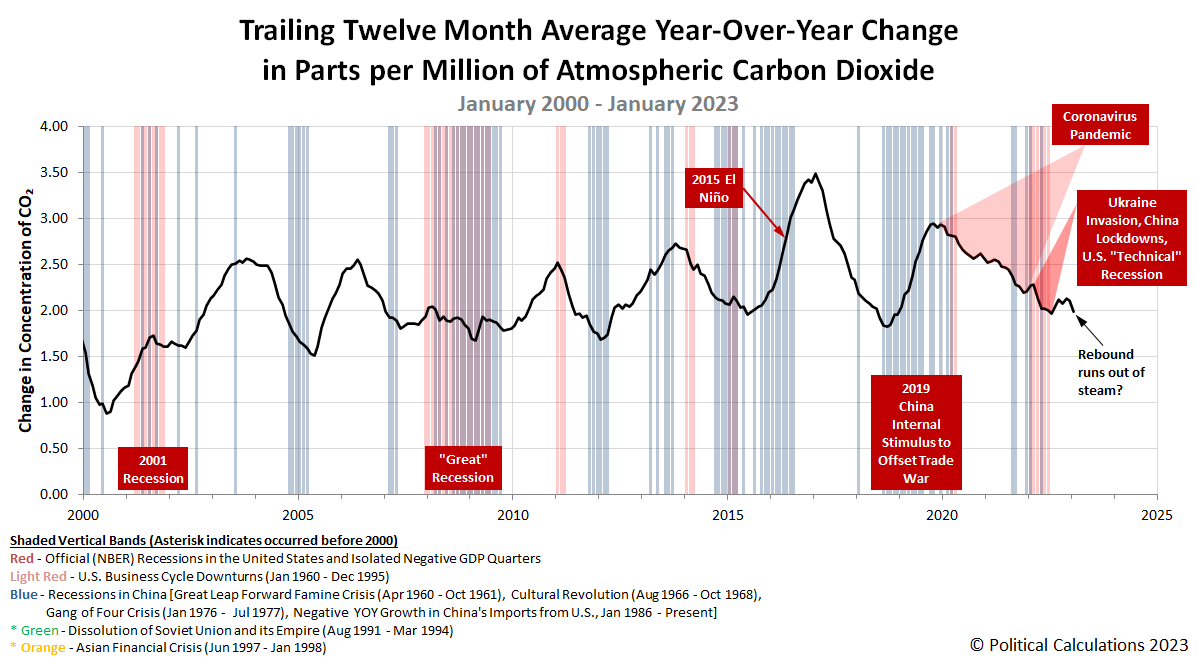
We're making a point of highlighting China's outsized role in contributing to global carbon dioxide emissions because its shows up in measurements of the concentration of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere, which increasingly tells us quite a lot about the state of China's economy. In February 2023, those measurements provide more evidence that the Chinese government's zero-COVID lockdowns during the final three months of 2022 negatively impacted its economy.
Changes in China's economic growth drive changes in the country's CO₂ emissions, which are typically reflected in atmospheric concentration data measured at high-elevation observatories on the big island of Hawaii some 4-6 weeks later after they've fully diffused into the Earth's air. What that data indicates is that China's zero-COVID lockdowns, which were ramped up during the fourth quarter of 2022, effectively reversed much of the third-quarter's rebound.
Looking forward, we should see the pace at which CO₂ accumulates in the atmosphere reverse once again and start to increase. That change will coincide with increased economic output in China following its government's complete reversal of its zero-COVID policy and its lifting of lockdowns at the end of December 2022.
References
National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. Earth System Research Laboratory. Mauna Loa Observatory CO2 Data. [Text File]. Updated 6 February 2023. Accessed 6 February 2023.
Global Carbon Project. (2022). Supplemental data of Global Carbon Budget 2022 (Version 1.0) [Data set]. Global Carbon Project. DOI: 10.18160/gcp-2022.