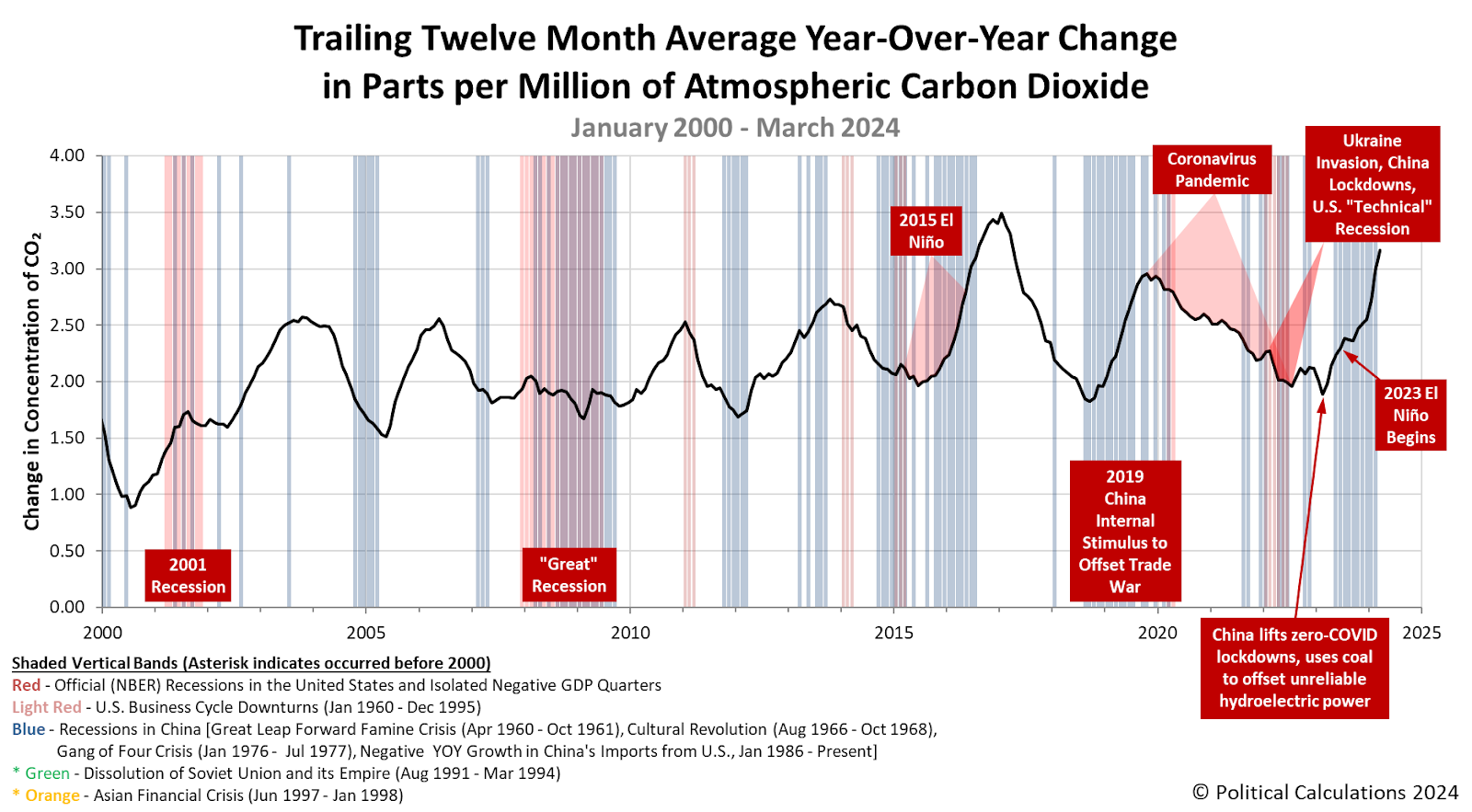
The first quarter of 2024 has come and gone. Along the way, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere has been rising at one of the fastest clips on record.
That observation is a good sign of the extent to which China, the worlds's biggest consumer of coal and the world's biggest producer of carbon dioxide emissions, is pushing to grow its economy.
But China isn't alone in increasing its emissions at such a fast rate. India is also boosting its consumption of coal and its emissions of carbon dioxide to power its economic growth.
Together, the two most populous nations in the world are leaving their mark on the Earth's atmosphere. That mark can be seen in the rate at which carbon dioxide is being added to the Earth's atmosphere, which we measure as the trailing twelve month average of the year-over-year change in the concentration of CO₂ in the air as measured at the remote Mauna Kea Observatory. The following chart shows how that measure has evolved from January 2000 through March 2024:
The rapid rise in the pace at which carbon dioxide accumulates in the atmosphere during the first quarter of 2024 can be traced to the increased coal consumption of both China and India.
China and India lifted imports of seaborne thermal coal to three-month highs in March as the world's two biggest buyers took advantage of lower international prices of the fuel to meet strong domestic power demand....
For the first quarter, China's seaborne imports of the grade of coal used mainly to generate electricity were 80.64 million tons, up 17.2% from the 68.82 million recorded in the same period in 2023.
The strength in China's imports is being driven by a combination of strong growth in power demand and by seaborne prices being competitive with domestic coal.
Official data showed China's power consumption was 11% higher in January and February this year compared to the same months in 2023, and power generation rose 6.9% in 2023, outpacing the 5.2% growth rate for the economy as a whole.
China's electricity demand is being boosted by a variety of factors, including increasing electrification of the vehicle fleet, higher demand from air conditioners and appliances, and increased electrification of industrial processes, such as some types of smelting.
The article notes China imported some 29.7 million metric tons of coal in March 2024, almost double India's coal imports. India is the world's second-biggest buyer of coal.
Overall, the portion of excess carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere generated by China is on pace to exceed the United States' residual historic CO₂ emissions before the end of the decade.
References
National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. Earth System Research Laboratory. Mauna Loa Observatory CO2 Data. [Online Data]. Updated 5 April 2024.
Image credit: Damn that Smoke (Suzhou, China) by DaiLui on Flickr. Creative Commons CC by 2.0 Deed Attribution 2.0 Generic.