Those who follow our analysis on a regular basis already know that we consider the number of seasonally-adjusted initial unemployment insurance claims filed each week to be the most easy-to-accurately-predict number in all of economic datadom.
 The reason why is because the weekly data tends to follow a straight-line path over time, with the variation in the data from week-to-week about these linear trends being easily described by a normal, bell-curve kind of statistical distribution.
The reason why is because the weekly data tends to follow a straight-line path over time, with the variation in the data from week-to-week about these linear trends being easily described by a normal, bell-curve kind of statistical distribution.
Periodically, breaks in existing trends occur and new trends begin, which we are able to identify using the kind of statistical analysis that has been successfully and widely applied in manufacturing or industrial applications for over 80 years.
Here, we recognize that the cause of a break in an existing trend in the weekly jobless claims data is actually triggered by events that significantly altered the business outlook for employers some 2-3 weeks earlier in time, which corresponds to the employers implementing their decisions affecting their employee retention plans with their next pay cycle. Since most employed Americans are paid on either a weekly or biweekly basis, that works out to a two-to-three week lag from when an event significantly affecting the pace of layoffs in the U.S. occurs, to when the effects of such a change in the business outlook of employers shows up in the BLS' weekly data reports.
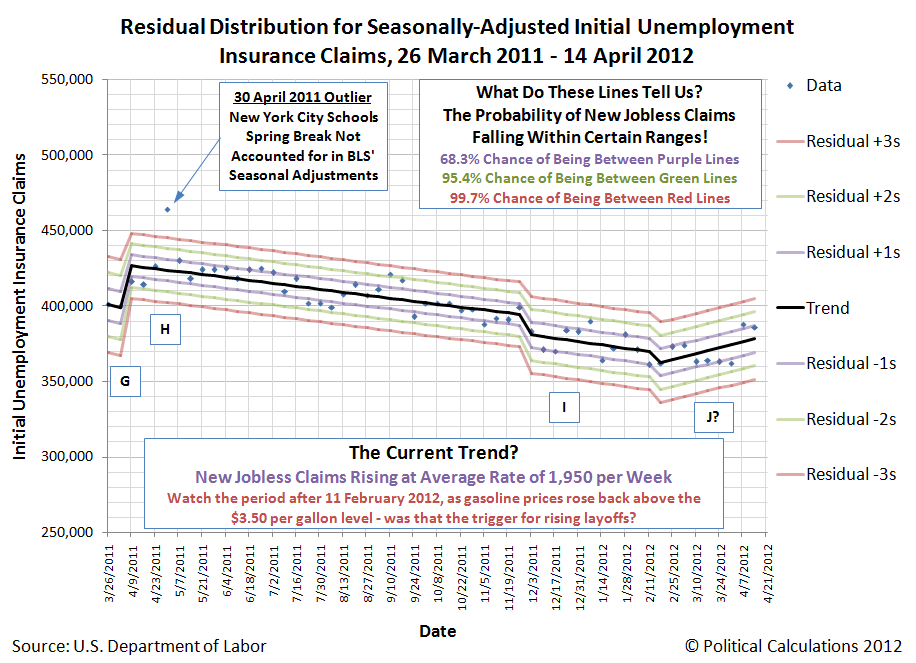
With that in mind, we're going to present two possible hypotheses behind what's affecting the level of claims filed for new unemployment benefits that are being filed today. Here, we begin with what we describe as the "current" trend, which we've previously identified began on 3 December 2011, as the average price for gasoline in the United States fell below $3.50 per gallon two-to-three weeks earlier. In our first chart, we assume that trend is still in effect:
Here, our first hypothesis of what's behind the changes we're now observing for new jobless claims is that that previous improvement we've seen in the number of new claims filed for recently laid off employees is in the process of flattening out at a level somewhere between 370,000 and 380,000 claims each week. We note that level of new jobless claims is some 60,000-70,000 higher than the average level that was typical in the years preceding the December 2007 recession and would be consistent with a permanently higher unemployment rate than the 4.7% that was recorded in the U.S. during that time.
For our second chart, our hypothesis is that the increase in the national average of gasoline prices in the United States back above the $3.50 per gallon mark in the final week of January 2012, the effects of which would show up in the weekly data after 11 February 2012, has perhaps initiated a new, but increasing trend in the number of new jobless claims being filed each week:
And that's where we are today in our thinking. We should know sometime this summer (and hopefully sooner) which of our two hypotheses has turned out to be true, or if another hypothesis might perhaps better describe what is happening with the number of new jobless benefit claims being filed each week.
Welcome to the blogosphere's toolchest! Here, unlike other blogs dedicated to analyzing current events, we create easy-to-use, simple tools to do the math related to them so you can get in on the action too! If you would like to learn more about these tools, or if you would like to contribute ideas to develop for this blog, please e-mail us at:
ironman at politicalcalculations
Thanks in advance!
Closing values for previous trading day.
This site is primarily powered by:
CSS Validation
RSS Site Feed
JavaScript
The tools on this site are built using JavaScript. If you would like to learn more, one of the best free resources on the web is available at W3Schools.com.